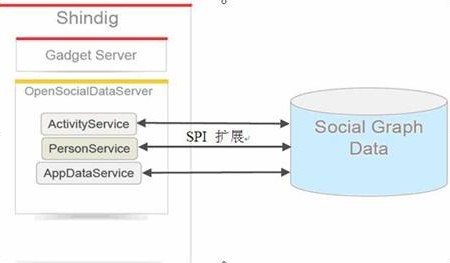
Shindig 服务器端 SPI 扩展
Shindig 作为 OpenSocial 规范的引用实现,提供了 SPI 的扩展能力,允许你把数据适配到 Shindig 容器中去。你的这些数据也许存在于诸如 My SQL/Oracle 的关系数据库,或者是以 JSON 格式存储的静态文件,无论哪种存储,你都可能通过 Shindig SPI 将它们适配到 Shindig, 从而使这些数据公布在 OpenSocial 平台上。
图 4. Shindig SPI 扩展
如图 4 所示,你的应用需要实现 ActivityService, PersonService, AppDataService 三个接口,利用诸如 JDBC/Hibernate 等机制把数据提供给 Shindig。
接下来,本文将通过一个例子,实现 PersonService 接口向 Shindig 提供 People/Friends 相关的 OpenSocial 数据。
清单 1 是 SocialTestJsonPersonService类的实现。
清单 1. SocialTestJsonPersonService Class
private static final String PEOPLE_TABLE = "people";
private static final String FRIEND_LINK_TABLE = "friendLinks";
private JSONObject db;
private BeanConverter converter;
……
public Future<RestfulCollection<Person>> getPeople(Set<UserId>
userIds,GroupId groupId, CollectionOptions options, Set<String> fields,
SecurityToken token) throws ProtocolException {
List<Person> result = Lists.newArrayList();
try {
//Read people data from JSON table.
JSONArray people = db.getJSONArray(PEOPLE_TABLE);
Set<String> idSet = getIdSet(userIds, groupId, token);
for (int i = 0; i < people.length(); i++) {
JSONObject person = people.getJSONObject(i);
if (!idSet.contains(person.get(Person.Field.ID.toString()))) {
continue;
}
// Add group support later
Person personObj = filterFields(person, fields, Person.class);
result.add(personObj);
}
if (GroupId.Type.self == groupId.getType() && result.isEmpty()) {
throw new ProtocolException(HttpServletResponse.SC_BAD_REQUEST,
"Person not found");
}
int totalSize = result.size();
return ImmediateFuture.newInstance(new RestfulCollection<Person>(
result, options.getFirst(), totalSize, options.getMax()));
} catch (JSONException je) {
throw new ProtocolException(
HttpServletResponse.SC_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR, je
.getMessage(), je);
}
}
public Future<Person> getPerson(UserId id, Set<String> fields,
SecurityToken token) throws ProtocolException {
try {
//Read people data from JSON table.
JSONArray people = db.getJSONArray(PEOPLE_TABLE);
for (int i = 0; i < people.length(); i++) {
JSONObject person = people.getJSONObject(i);
if (id != null
&& person.get(Person.Field.ID.toString()).equals(
id.getUserId(token))) {
Person personObj = filterFields(person, fields,
Person.class);
return ImmediateFuture.newInstance(personObj);
}
}
throw new ProtocolException(HttpServletResponse.SC_BAD_REQUEST,
"Person not found");
} catch (JSONException je) {
throw new ProtocolException(
HttpServletResponse.SC_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR, je
.getMessage(), je);
}
}
……
}
从清单 1 可以看到,SocialTestJsonPersonService 实现了 PersonService 两个接口方法 getPeople 及其 getPerson。getPeople 根据传入参数 userIds,返回相应于该 ID 列表的用户列表,而 getPerson 根据传入参数 id,返回相应于该 ID 的用户。
注意,Shindig 依赖 Guice 做动态的依赖注入 (dependency Injection),我们需要在 org.apache.shindig.social.sample.SampleModule 里指示 Guice 把 PersonService 绑定到 SocialTestJsonPersonService 实现,如清单 2 所示:
清单 2. SampleModule Class
@Override
protected void configure() {
super.configure();
bind(String.class).annotatedWith(Names.named("shindig.canonical.json.db"))
.toInstance("sampledata/canonicaldb.json");
bind(String.class).annotatedWith(Names.named("shindig.socialtest.json.db"))
.toInstance("sampledata/socialtestdb.json");
bind(ActivityService.class).to(JsonDbOpensocialService.class);
bind(AppDataService.class).to(JsonDbOpensocialService.class);
//bind(PersonService.class).to(JsonDbOpensocialService.class);
bind(PersonService.class).to(SocialTestJsonPersonService.class);
bind(MessageService.class).to(JsonDbOpensocialService.class);
bind(OAuthDataStore.class).to(SampleOAuthDataStore.class);
// We do this so that jsecurity realms can get access to the jsondbservice singleton
requestStaticInjection(SampleRealm.class);
}
……
}
从清单 2 中,还可以看到,标记为"shindig.socialtest.json.db"的字符串绑定到了"sampledata/socialtestdb.json", socialtestdb.json 是我们示例中的 JSON 数据文件,用来保存 People 数据。在 SocialTestJsonPersonService 的实现中,db.getJSONArray(PEOPLE_TABLE) 就是从该 JSON 文件获取所有的 People 数据。
在下一节,我们给出客户端实现,来消费 socialtestdb.json 中的 Social 数据。