此例程包括两个部分,分别演示可编程安全性和调用者身份传播。
可编程安全性例程
可编程安全性可应用在web层和EJB层,分别是通过javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest接口的isUserInRole ()、getUserPrincipal ()方法和javax.ejb.EJBContext接口的isCallerInRole ()、getCallerPrincipal ()方法来实现的。 public boolean isUserInRole(java.lang.String role)方法此方法用来判断调用者是否属于某一特定的安全角色,如果属于返回true,否则返回false。参数role指定某一安全角色。通过此方法开发者可以在程序代码中加入自己的安全逻辑判断,从而增强了J2EE在安全方面的灵活性。
public java.security.Principal getUserPrincipal()方法调用此方法可以得到一个java.security.Principal对象,此对象包含了调用者的用户名,通过Principal.getName()方法可以得到用户名。通过调用getUserPrincipal()方法开发者可以得到调用者的用户名,然后对调用者的用户名进行特定的逻辑判断。
public java.security.Principal getCallerPrincipal()方法 和public boolean isCallerInRole(java.lang.String roleName)方法的作用和方法同上。
下面我们通过例程来演示这些方法的用法
程序清单:
2 <html>
3 <head><title>JSP Page</title></head>
4 <body>
5 <%-- <jsp:useBean id="beanInstanceName" scope="session" class="package.class" /> --%>
6 <%-- <jsp:getProperty name="beanInstanceName" property="propertyName" /> --%>
7 Hello!
8 the caller is <%=request.getUserPrincipal().getName()%><br/> <%--得到调用者的用户名--%>
9 <% if (request.isUserInRole("admin")){%> <%--判断调用者是否属于"admin"安全角色--%>
10 the caller is admin Role;
11 <%} %>
12 </body>
13 </html>
14 web.xml
15 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
16 <!DOCTYPE web-app PUBLIC
17 '-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD Web Application 2.3//EN'
18 'http://java.sun.com/dtd/web-app_2_3.dtd'>
19 <web-app>
20 <display-name>WebApp</display-name>
21 <servlet>
22 <servlet-name>webtest</servlet-name>
23 <display-name>webtest</display-name>
24 <jsp-file>/webtest.jsp</jsp-file>
25 <security-role-ref>
26 <role-name>adminref</role-name>
27 <role-link>admin</role-link>
28 </security-role-ref>
29 <security-role-ref>
30 <role-name>guestref</role-name>
31 <role-link>guest</role-link>
32 </security-role-ref>
33 </servlet>
34 <session-config>
35 <session-timeout>30</session-timeout>
36 </session-config>
37 <welcome-file-list>
38 <welcome-file>webtest.jsp</welcome-file>
39 </welcome-file-list>
40 <security-constraint>
41 <web-resource-collection>
42 <web-resource-name>WRCollection</web-resource-name>
43 <url-pattern>/webtest.jsp</url-pattern>
44 <http-method>GET</http-method>
45 <http-method>POST</http-method>
46 </web-resource-collection>
47 <auth-constraint>
48 <role-name>admin</role-name>
49 <role-name>guest</role-name>
50 </auth-constraint>
51 <user-data-constraint>
52 <transport-guarantee>NONE</transport-guarantee>
53 </user-data-constraint>
54 </security-constraint>
55 <login-config>
56 <auth-method>BASIC</auth-method>
57 <realm-name></realm-name>
58 </login-config>
59 <security-role>
60 <role-name>admin</role-name>
61 </security-role>
62 <security-role>
63 <role-name>guest</role-name>
64 </security-role>
65 </web-app>
66
从web.xml文件的内容可以看出,只有安全角色为"admin"和"guest"的用户才有权对webtest.jsp文件进行POST和GET操作。
运行结果:
创建一个web应用,将webtest.jsp作为一个web组件,并按照web.xml的内容配置web应用,在运行环境中将用户j2ee分配为admin安全角色,将用户Tony分配为guest角色。发布web应用到本地j2ee Server上。用ie访问webtest.jsp 如图17用用户j2ee的身份进行验证,用户j2ee属于admin安全角色。显示结果见图18
图17
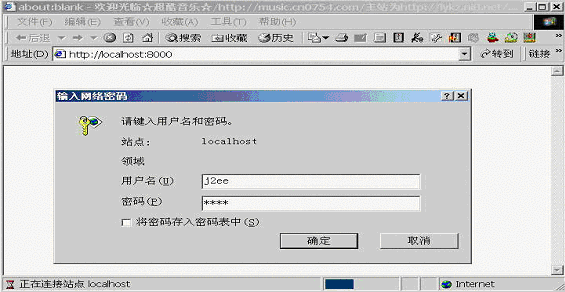
图18
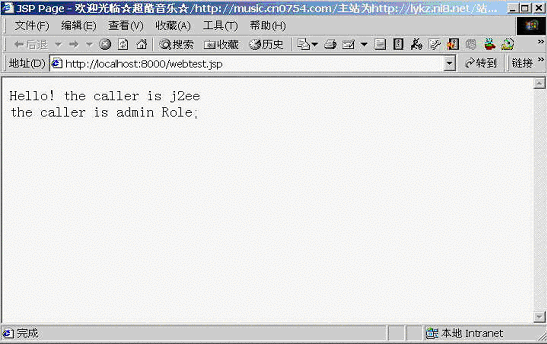
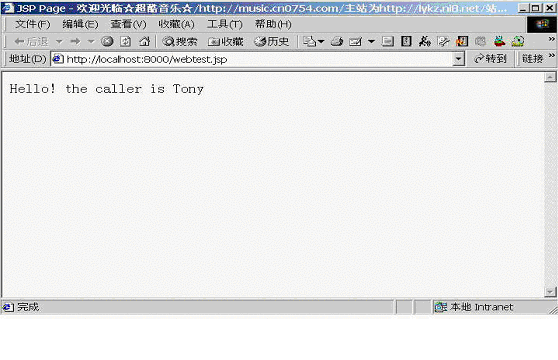
如果用用户Tony进行验证,结果见图19
图19
ejb中应用可编程的安全性与在web中的方法相似,本文不再进行介绍
传播调用者身份标识例程
本例程将演示调用者身份标识如何在调用链中传递的,并且介绍如何应用"Run As"来实现在调用链中更改调用者的身份。本例将用一个web组件(一个jsp文件)和两个ejb组件来形成一个调用链。
程序清单:
webtest.jsp
2 <%@page import="andy.*"%>
3 <%@page import="javax.naming.*"%>
4 <html>
5 <head><title>JSP Page</title></head>
6 <body>
7 <%-- <jsp:useBean id="beanInstanceName" scope="session" class="package.class" /> --%>
8 <%-- <jsp:getProperty name="beanInstanceName" property="propertyName" /> --%>
9 Hello!
10 the caller is <%=request.getUserPrincipal().getName()%> <br/>
11 <% if (request.isUserInRole("admin")){%>
12 the caller is admin Role;
13 <%} %>
14 <%
15 try {
16 Context ctx = new InitialContext();
17 andy.CountHome home =
18 (andy.CountHome)javax.rmi.PortableRemoteObject.narrow(
19 ctx.lookup("java:comp/env/CountHome"), andy.CountHome.class);
20 andy.Count count = home.create(1);
21 count.count();
22 }catch (Exception e)
23 {
24 e.printStackTrace();
25 }
26 %>
27 </body>
28 </html>
29
CountBean.java
2 import javax.ejb.*;
3 import javax.naming.*;
4 public class CountBean implements SessionBean {
5 public int val;
6 private SessionContext EjbCxt = null;
7 public int count()
8 {
9 int temp = 0;
10 System.out.println("CountBean.count()");
11 //打印调用者名
12 System.out.println("the caller is "+EjbCxt.getCallerPrincipal().getName());
13 //判断调用者的安全角色
14 if(EjbCxt.isCallerInRole("adminref")) // adminref为安全角色admin的引用名
15 {
16 System.out.println("the caller is admin Role");
17 }
18 if(EjbCxt.isCallerInRole("guestref")) // guestref为安全角色guest的引用名
19 {
20 System.out.println("the caller is guest Role");
21 }
22 if(EjbCxt.isCallerInRole("userref")) // userref为安全角色user的引用名
23 {
24 System.out.println("the caller is user Role");
25 }
26 //调用另一个ejb的远程方法
27 try {
28 Context ctx = new InitialContext();
29 CountHome1 home =
30 (CountHome1)javax.rmi.PortableRemoteObject.narrow(
31 ctx.lookup("java:comp/env/CountHome1"), CountHome1.class);
32 Count1 count = home.create(1);
33 temp = count.count();
34 }catch (Exception e)
35 {
36 e.printStackTrace();
37 }
38 return ++temp;
39 }
40 public void ejbCreate(int val) throws CreateException {
41 this.val = val;
42 }
43 public void ejbRemove() {
44 }
45 public void ejbActivate() {
46 }
47 public void ejbPassivate() {
48 }
49 public void setSessionContext(SessionContext ctx) {
50 EjbCxt = ctx; //获取EjbContext对象
51 }
52 }
53 CountBean1.java
54 package andy;
55 import javax.ejb.*;
56 public class CountBean1 implements SessionBean {
57 public int val;
58 private SessionContext EjbCxt = null;
59 public int count() {
60 System.out.println("CountBean1.count()");
61 System.out.println("the caller is "+EjbCxt.getCallerPrincipal().getName());
62 if(EjbCxt.isCallerInRole("adminref"))
63 {
64 System.out.println("the caller is admin Role");
65 }
66 if(EjbCxt.isCallerInRole("guestref"))
67 {
68 System.out.println("the caller is guest Role");
69 }
70 if(EjbCxt.isCallerInRole("userref"))
71 {
72 System.out.println("the caller is user Role");
73 }
74
75 return ++val;
76 }
77 public void ejbCreate(int val) throws CreateException {
78 this.val = val;
79 }
80 public void ejbRemove() {
81 }
82 public void ejbActivate() {
83 }
84 public void ejbPassivate() {
85 }
86 public void setSessionContext(SessionContext ctx) {
87 EjbCxt = ctx;
88 }
89 }
90
以上的三个文件分别是一个web组件和两个ejb组件的源代码,这三个组件构成了一个调用链.webtest.jsp中,首先通过HttpServletRequest..getUserPrincipal ()方法来得到调用webtest.jsp的用户的Principal对象,在通过Principal.getName()方法得到调用者的用户名. 然后通过HttpServletRequest..isUserInRole()方法来判断调用这是否属于特定的安全角色.CountBean是一个stateful SessoinBean,它拥有一个count()远程方法,在这个远程方法中写了用于得到调用者用户名和判断调用这安全角色的代码,还包括调用CountBean1对象的代码,用于展示调用者身份标识是如何在调用链中传递和调用者的安全角色如何被改变的.CountBean1也是一个stateful SessoinBean,它的代码内容与CountBean基本相同,只不过它不包含调用其他Bean的代码.
现在我们应该配置各组件的安全属性了.我们在组件webtest中创建安全角色admin,引用名为adminref,在组件CountBean和CountBean1中分别创建安全角色admin和user, 引用名分别为adminref和userref.将webtest组件配置为"HTTP Basic Authentication",给安全角色admin赋予访问webtest.jsp的权限.把CountBean设置为Run As Specified Role,选择user安全角色.在运行环境中将用户j2ee赋予admin安全角色和user安全角色.然后发布应用到服务器.用用户j2ee访问webtest.jsp.
执行结果:
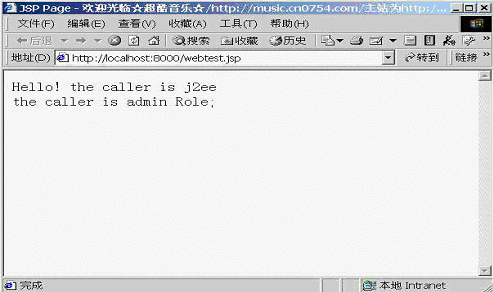
客户端见图20
图20
服务器端:
CountBean.count()
the caller is j2ee
the caller is admin Role
CountBean1.count()
the caller is j2ee
the caller is user Role
从运行结果看,访问webtest.jsp的用户为j2ee,其安全角色为admin,访问CountBean的用户名为j2ee,安全角色为admin.可以看到用户身份标识从web容器传递到了ejb容器.再看组件CountBean1的输出结果,由于CountBean被设置成了Run As Specified Role,因此在CountBean向下调用其他组件对象时,用户安全角色已经被改为指定的安全角色,这里是user.所以我们会看到,调用组件CountBean1的用户名为j2ee,安全角色为user.j2ee的这种安全特性满足了同一用户在不同应用中具有不同安全角色的需求.开发人员也可以利用这种特性进行灵活的安全逻辑判断.


