【IT168技术】本地数据库非常好的实践。将从三个方面来讨论如何改善wp数据库应用在速度及内存消耗方面的性能。不仅要改善程序的性能而且要量化到具体改善了多少。
关于提升应用性能最重要的技术是:
在实体类中定义版本列 ColumnAttribute.IsVersion
在实体类中实现INotifyPropertyChanging
使用编译查询
首先,建立一个WP7.1应用。首先创建一个测试设置,这将是我们的测试和测量基准线。我们将使用下面的类,不做任何改善,作为本地数据库的性能测试基准:
public class PersonSimple : IPerson
{
[Column(IsPrimaryKey = true, IsDbGenerated = true)]
public int ID
{
get;
set;
}
[Column(CanBeNull = false)]
public string FirstName
{
get;
set;
}
[Column(CanBeNull = false)]
public string LastName
{
get;
set;
}
[Column(CanBeNull = false)]
public int Age
{
get;
set;
}
[Column(CanBeNull = true)]
public string Address
{
get;
set;
}
[Column(CanBeNull = true)]
public string Email
{
get;
set;
}
[Column(CanBeNull = true)]
public string WebSite
{
get;
set;
}
}
我们使用 IPerson 接口,通过同样的泛型代码来测试不同版本Person类
public interface IPerson
{
string FirstName { get; set; }
string LastName { get; set; }
int Age { get; set; }
string Address { get; set; }
string Email { get; set; }
string WebSite { get; set; }
}
除 PersonSimple 测试设置还包括:
1. 下面两个增强版本
PersonVersioned: with added an additional version column(含版本列)
PersonOptimized: with version column and implemented INotifyPropertyChanging (包含版本列并且实现INotifyPropertyChanging)
2. 对于上述三类Person,分别对应数据库中三个独立的表,分别被初始化存放10000条记录
3. (为了测试版本列及INotifyPropertyChanging,分别更改第50行记录的FirstName和LastName。泛型方法如下)
private long UpdatePersonEntities(Func> getCollection) where T : class, IPerson, new()
{
long elapsedMilliseconds;
using (PersonDataContext context = new PersonDataContext(ConnectionString))
{
Table collection = getCollection(context);
List personList = collection.ToList();
int count = personList.Count;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
if ((i % 50) != 0)
{
continue;
}
IPerson person = personList[i];
person.FirstName = string.Concat(person.FirstName, "changed");
person.LastName = string.Concat(person.LastName, "changed");
//person.Age = person.Age + 1;
//person.Address = string.Concat(person.Address, "changed");
//person.Email = string.Concat(person.Email, "changed");
//person.WebSite = string.Concat(person.WebSite, "changed");
}
Debug.WriteLine("Update {0} entities...", count);
Stopwatch stopwatch = Stopwatch.StartNew();
// save changes to the database
context.SubmitChanges();
stopwatch.Stop();
elapsedMilliseconds = stopwatch.ElapsedMilliseconds;
Debug.WriteLine("Time elapsed: {0} ms", elapsedMilliseconds);
}
return elapsedMilliseconds;
}
总之,这种方法试图重现这两种技术的性能改进的情况。
这种优化是关于Windows Phone 的 LINQ To SQL
public class PersonVersioned : IPerson
{
[Column(IsVersion = true)]
private Binary version;
// More code here...
}
本优化可以对大量数据更新产生性能改进。
通过维护一个实例的两个副本跟踪变化。一个副本表示从数据库中取出后的原始状态,另一个表示应用程序的操作更改。当更改被提交到数据库时,LINQ to SQL可以判断哪些已经被更新,并且仅更新哪些发生改变的。
默认情况下,LINQ to SQL为属性创建两个副本。然而,通常情况下,只有集合中的少数对象会在特定操作中被修改。因此,就没必要再保存第二个副本了。
可以使程序修改属性时通知DataContext。DataContext可以像触发器一样使用这些通知创建副本。这样,只有发生更改的属性需要第二个副本,这将减少内存占用
public class PersonOptimized : IPerson, INotifyPropertyChanging
{
private int id;
private string firstName;
private string lastName;
private int age;
private string address;
private string email;
private string webSite;
[Column(IsVersion = true)]
private Binary version;
[Column(IsPrimaryKey = true, IsDbGenerated = true)]
public int ID
{
get
{
return this.id;
}
set
{
if (this.id != value)
{
this.OnPropertyChanging("ID");
this.id = value;
}
}
}
//...
//More code...
}
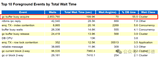
测试结果:
PersonSimple:
更新前内存使用:11560 KB
更新后内存使用:22092 KB
更新使用内存: 10532 KB
更新耗时: 2082 ms
PersonVersioned:
更新前内存使用:12580 KB
更新后内存使用:20244 KB
更新使用内存: 7664 KB
更新耗时: 1278 ms
PersonOptimized:
更新前内存使用:12932 K
更新后内存使用:B16264 KB
更新使用内存: 3332 KB
更新耗时: 326 ms
Compiled Query Tests
What is Compiled Query?
默认情况下,查询执行时LINQ to SQL将LINQ表达式树翻译为对应的T-SQL语句,对于经常执行的查询(例如,根据ID查找相应记录),每次生成相应的T-SQL的开销是非常浪费的。为了避免这种低效,可以使用编译查询。编译查询提前生成带参数的T-SQL语句,然后可以带入不同的参数值重用已生成的T-SQL语句。
private void btnTestCompiledQuery_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
Func> getPeopleByAddress =
CompiledQuery.Compile((PersonDataContext context, string addressQuery, int age) =>
from p in context.PeopleSimple where p.Address.Contains(addressQuery) && p.Age > age select p);
int count = 100;
long millisecondsCompiled;
long millisecondsQuery;
using (PersonDataContext context = new PersonDataContext(ConnectionString))
{
Debug.WriteLine("Start compiled query test...");
Stopwatch stopwatch = Stopwatch.StartNew();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
var peopleByAddressQuery = getPeopleByAddress(context, i.ToString(), i);
//execute query
PersonSimple personByAddress = peopleByAddressQuery.FirstOrDefault();
}
stopwatch.Stop();
millisecondsCompiled = stopwatch.ElapsedMilliseconds;
Debug.WriteLine("Time elapsed: {0} ms", millisecondsCompiled);
Debug.WriteLine("Start normal query test...");
stopwatch = Stopwatch.StartNew();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
var peopleByAddressQuery = from p in context.PeopleSimple where p.Address.Contains(i.ToString()) && p.Age > i select p;
//execute query
PersonSimple personByAddress = peopleByAddressQuery.FirstOrDefault();
}
stopwatch.Stop();
millisecondsQuery = stopwatch.ElapsedMilliseconds;
Debug.WriteLine("Time elapsed: {0} ms", millisecondsQuery);
}
StringBuilder messageBuilder = new StringBuilder();
messageBuilder.AppendFormat("Get people by age normal: {0} ms", millisecondsQuery).AppendLine();
messageBuilder.AppendFormat("Get people by age compiled: {0} ms", millisecondsCompiled).AppendLine();
MessageBox.Show(messageBuilder.ToString());
}
stopwatch.Stop();
millisecondsQuery = stopwatch.ElapsedMilliseconds;
Debug.WriteLine("Time elapsed: {0} ms", millisecondsQuery);
}
StringBuilder messageBuilder = new StringBuilder();
messageBuilder.AppendFormat("Get people by age normal: {0} ms", millisecondsQuery).AppendLine();
messageBuilder.AppendFormat("Get people by age compiled: {0} ms", millisecondsCompiled).AppendLine();
MessageBox.Show(messageBuilder.ToString());
}
查询结果
非编译查询耗时: 701 ms
编译查询耗时: 501 ms
Conclusion
总之,我们已经证明,所有这三种方法显着提高性能。我们甚至惊喜,只需添加一个版本列就有30%左右的内存使用率改善以及40%的速度提升 。
Here are the results for the version column and INotifyPropertyChanging techniques combined in a chart: